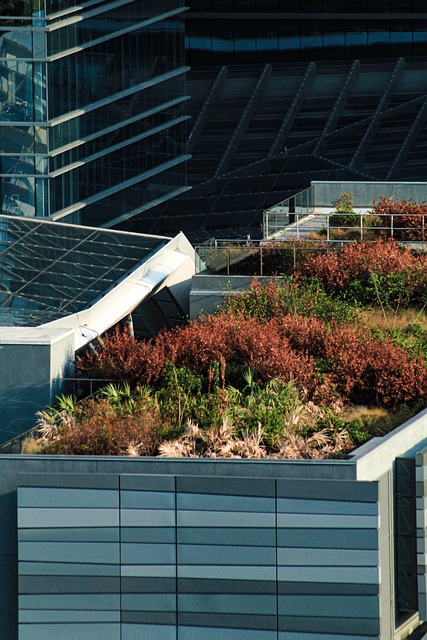
Green, vegetation-covered rooftops are a popular way to reduce energy consumption and improve indoor comfort. But how does a simple layer of greenery reduce strain on HVAC systems and contribute to cleaner air? Whether you’re a homeowner, business owner, or sustainability enthusiast, understanding these benefits can help you make informed choices about more efficient buildings.
What Are Green Roofs?
Planting greenery on a roof will provide environmental advantages while enhancing a building’s energy efficiency. Unlike traditional roofs made of concrete, metal, or shingles, green roofs consist of layers that support plant life, including a waterproof section, drainage system, soil, and carefully selected vegetation.
There are two types of green roofs.
- Extensive green roofs are lightweight, needing minimal maintenance and a shallow layer of soil about two to six inches thick. They usually have hardy, low-growing plants like grass, which makes them cost-effective and practical.
- Intensive green roofs function more like a rooftop lawn, with deeper soil layers that support the growth of a broader variety of plants like shrubs and small trees. While they offer extra biodiversity and aesthetic appeal, they also require more structural support, irrigation and maintenance.
While the history of green roofs dates back millennia, modern green roofs have gained popularity as cities look for ways to improve their energy efficiency, reduce pollution, and create more sustainable urban environments.
Benefits of Green Roofs for HVAC Efficiency
While green roofs have not gained popularity to the point of ubiquity, they’ve made a comeback due to their multiple advantages.
- Noise reduction: If you live in a multi-tenant building, you might know the pain of noise pollution ruining a good night’s sleep or walking on tiptoes so you don’t wake up your neighbors. Green roofs absorb sound while providing insulation.
- Increased biodiversity: A green roof is an excellent way to add biodiversity. Planting species that don’t live in your area may attract new insects, birds, and other small animals.
- Thermal regulation: Buildings with green roofs experience more consistent temperatures. The green roof reduces heat and cold transfer through the ceiling, keeping the rooms inside warm or cool as needed. Your HVAC system will not need to work as hard to maintain the desired temperature because the air cannot escape the space as easily.
- Longevity: Roofs with vegetation last longer than conventional roofs and need fewer repairs.
- Aesthetics: A green roof is an aesthetically pleasing way to become more sustainable. A roof filled with thriving plant and animal life is more attractive than standard shingles or tiles.
How Do Green Roofs Improve Energy Efficiency?
Green roofs significantly improve the efficiency of heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems by reducing their workload. Since HVAC units regulate indoor temperatures, filter air, and maintain comfort, any factor stabilizing indoor conditions can lead to better performance and lower energy consumption.
Green roofs do all those things by acting as natural insulators and cooling systems, ultimately boosting HVAC performance in multiple ways.
- Less strain on HVAC systems: A primary benefit of green roofs is their ability to maintain more stable indoor temperatures. Traditional roofs absorb heat in the summer and lose heat in the winter, forcing HVAC systems to work harder to compensate. In contrast, green roofs create a buffer that minimizes temperature fluctuations, leading to lower energy consumption, reduced wear and tear on equipment components and extended heating and cooling equipment life spans.
- Lower cooling loads in summer: HVAC systems must work overtime to cool buildings in the heat, especially in urban areas. Green roofs absorb less heat than conventional roofing materials, naturally cooling the air around them. They result in less heat transfer into the building, reduced demand for air conditioning, and significant energy savings in cooling costs.
- Improved insulation for heating efficiency: Green roofs trap heat inside the building in colder months by providing an additional insulation layer. HVAC systems don’t have to work as hard to maintain warmth, reducing the need for excessive heating. The insulation also prevents heat loss through the roof, a significant energy waste source in traditional buildings.
- Balanced indoor humidity levels: HVAC systems also regulate humidity inside buildings. Green roofs contribute to this by absorbing and releasing moisture, preventing excessive dryness in winter, and reducing humidity buildup in summer. HVAC equipment can maintain indoor air quality more efficiently without overcompensating.
- Reduced HVAC costs: Since green roofs limit extreme temperature fluctuations, HVAC systems experience less strain and fewer breakdowns. That translates to fewer repairs and maintenance costs, a longer life span for HVAC units, and less frequent need for system replacements.
- Potential for smaller HVAC systems: Building owners with well-designed green roofs may even be able to install smaller, less powerful HVAC systems since they won’t require as much heating and cooling capacity. Significantly reduce upfront costs for new buildings and renovations.
How Do Green Roofs Improve Air Quality?
Green roofs are also crucial in enhancing air quality. In urban areas, air pollution from vehicles, industrial emissions, and HVAC exhaust can make outdoor and indoor air unhealthy to breathe. By adding a layer of vegetation to rooftops, green roofs filter pollutants, reduce carbon dioxide levels, and create a cleaner environment for buildings and cities.
- Filtering airborne pollutants: Unfortunately, nearly 80% of the U.S. population lives in areas with limited access to clean air. Green roofs contribute to a healthier urban environment as a living air filter, trapping harmful pollutants that would otherwise circulate through the atmosphere.
- Absorbing carbon dioxide and producing oxygen: Like trees and other plants, the vegetation on green roofs absorbs carbon dioxide and releases oxygen back into the air. This process combats rising carbon dioxide levels. A single green roof may not singlehandedly reverse pollution, but these systems can have a dramatic impact when installed across multiple buildings.
- Reducing HVAC-related air pollution: HVAC systems contribute to air pollution by consuming large amounts of energy. Since green roofs improve HVAC efficiency and reduce the need for excessive heating and cooling, they indirectly lower the emissions associated with electricity generation.
The Future of Sustainable Buildings
Green roofs are a practical solution for improving HVAC efficiency, reducing energy consumption, and enhancing air quality. By acting as natural insulators, they ease the workload on heating and cooling systems, lowering energy costs and extending the life span of HCAV equipment. At the same time, they filter pollutants, absorb carbon dioxide, and contribute to cleaner, healthier indoor and outdoor air. As cities grow and climate concerns become more prominent, green roofs offer a sustainable way to reduce heat, improve building performance, and create healthier living spaces. By adopting this innovative approach, you’re contributing to a greener, more sustainable future.
Beth Rush is the green wellness editor at Body+Mind. She has more than five years of experience writing and editing articles covering topics like sustainable transit and the importance of green spaces in urban planning. You can find Beth on Twitter @bodymindmag. Subscribe to Body+Mind for more posts by Beth!
Image by Marco Brugo